What is Terminal Blocks?Basics and Types
2014/09/09 SHINING E&E INDUSTRIAL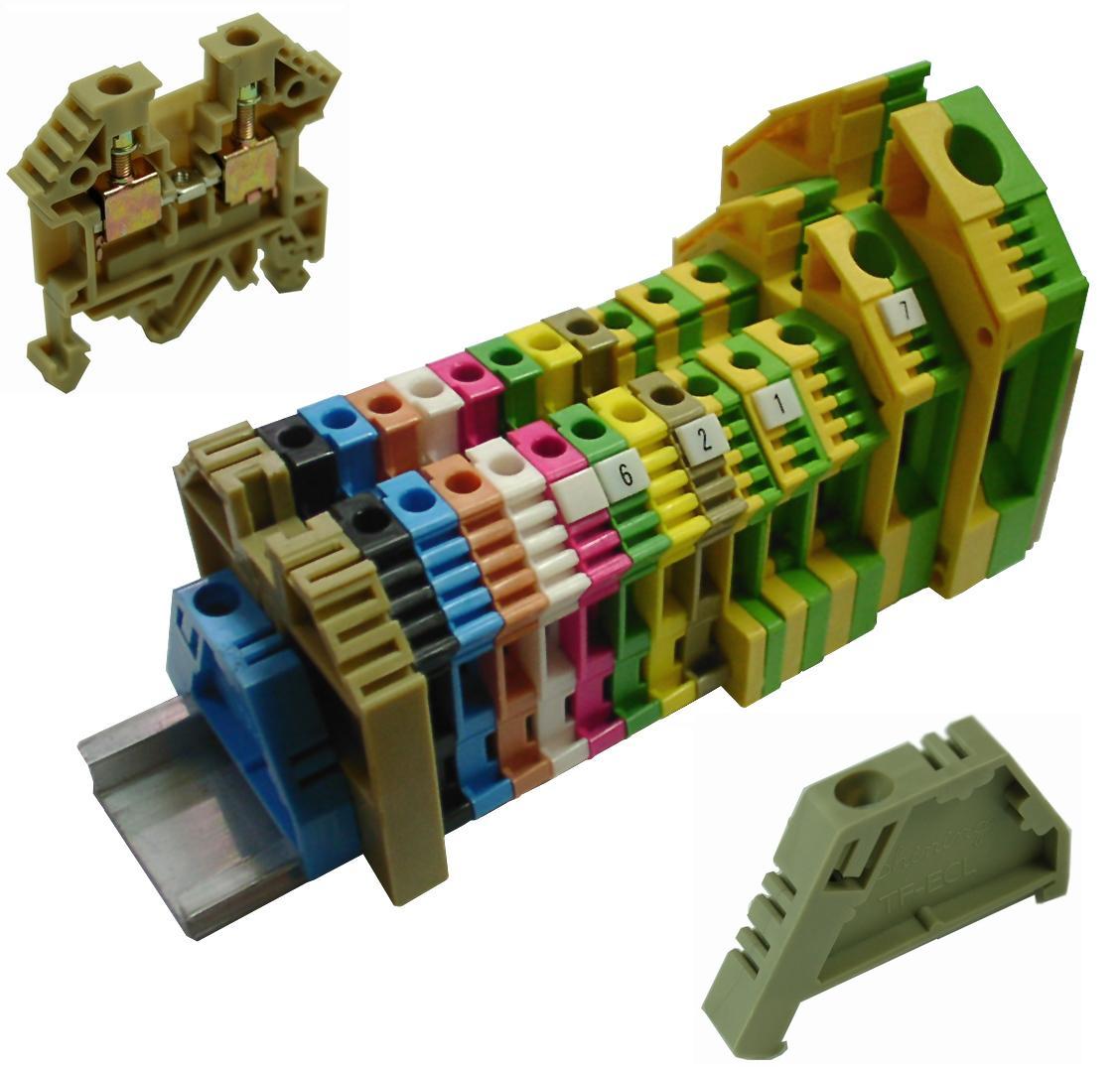
WHAT IS A TERMINAL BLOCK? HOW DOES A TERMINAL BLOCK WORK?
A terminal block, also known as a connection terminal, is a modular block used in electrical and electronics systems to connect and secure electrical wires or cables. It serves as a convenient and organized way to make electrical connections, whether for power distribution, signal routing, or control wiring. Terminal blocks work by guiding electrical current through an insulated structure, enabling multiple wires to operate concurrently in close proximity. When you have a set of electrical wires to connect, a terminal block provides a safe, convenient way to keep them organized. They are rugged, easy to use, and designed to keep wires of varying gauges securely connected.
WHAT IS A TERMINAL STRIP?
A terminal strip combines many similar terminal blocks in a single device, used for connecting the central panel and external devices. In a strip, the blocks are insulated from one another.
TERMINAL BLOCK SPECIAL FUNCTION
Generally, a terminal block is a set of two or more similar screw-down connection points. You can connect wires at these points. A terminal strip combines many similar blocks in a single device. In a strip, the blocks are insulated from one another. While most terminal blocks simply create an electrical connection, some have built-in fuse holders, indicator lamps, or other features that add functionality for more sophisticated applications.
Terminal Block Labeling
You can use a terminal block to organize wires having different functions. Many terminal blocks have a labeling scheme that lets you identify how the wires are organized.
ADVANTAGES OF TERMINAL BLOCKS
- Organize the wiring to improve panel space:Terminal strips provide a space-saving solution by allowing for a tidy and organized arrangement of wires. This makes it easier to access the wires when necessary, while also freeing up valuable panel space.
- Simplify assembly methods:Terminal strips simplify the assembly process by providing a quick and easy way to connect wires. This reduces the risk of errors during installation and also saves time and effort.
- Improve the electrical safety of the panel:Terminal strips help to improve electrical safety by reducing the risk of exposed wires, short circuits, and electrical shocks. They also help to prevent wiring errors, which can lead to dangerous electrical situations.
- Facilitate equipment maintenance and problem detection:Terminal strips make it easy to access and troubleshoot wires, which facilitates equipment maintenance and problem detection. This helps to reduce downtime and increase productivity, as well as making it easier to replace faulty components or upgrade equipment.
A terminal block's main functions are to connect and insulate. The main block body is made of tough material, such as plastic or ceramic, that electrically isolates adjacent blocks. The conducting parts are made of copper and corrosion-resistant metals compatible with copper.
HOW TO USE TERMINAL BLOCKS?
A terminal block must first be mounted in a safe, stable location away from moisture. To use it, strip about ½ inch of insulation from the two wires you want to connect. You then insert the bare wires into the block's metal connectors and screw them down until they're securely fastened.

IMPORTANT ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS FOR TERMINAL BLOCKS
- Terminal Block Orientation
Terminal blocks are commonly available with one of three different wire entry angles: 45°, 90°, or 180°. 90° and 180° types are also referred to as “horizontal” and “vertical”, respectively.
- Terminal Block Contact
When discussing terminal blocks, the term"contact", also known as a position, way, or pole, refers to a wire attached to the block. The number of contacts is an important specification when considering a product, as a buyer is required to match this number with the number of wires necessary for a project or application. This indicates how many individual circuits a terminal block can accommodate, ranging from a single pole to as many as 24 poles. SHINING can provide terminal blocks with 2 / 3 / 4 / 5 / 6 / 7 / 8 / 9 / 10 / 11 / 12 / 13 / 14 / 15 poles.

- Terminal Block Pitch
Pitch is the center-to-center distance between adjacent poles and affects factors like creepage, voltage/current, and clearance. Contact pitch is directly related to the number of contacts and is typically expressed in millimeters(mm). Common pitch values include 2.54 mm, 3.81 mm, and 5.0 mm.
- Terminal Block Current Rating
This measures the capacity of the terminal block to handle current safely. Select a module with a rating of at least 150% of your system's expected maximum current to avoid overheating and potential damage.
- Terminal Block Voltage Rating
Ensure the terminal block's voltage rating exceeds your system's maximum voltage, considering protection against voltage surges.
- Terminal Block Wire Size/Type
Terminal blocks specify wire size using American wire gauge (AWG) units. Check that the module can accommodate your wire size and type; most offer flexibility with a range of wire sizes (e.g., 184 AWG or 2412 AWG) and compatibility with stranded or single-core wire depending on the terminal block type.
These different types of terminal blocks allow for greater wiring flexibility and can meet various application needs.
You can find more information here: PANEL MOUNTED TERMINAL BLOCKS
TERMINAL BLOCK TYPE
You can find dozens of types of terminal blocks, some generic, some specialized. Designers have developed terminal blocks for household, industrial, electronic, and many other uses.
STRUCTURE TYPE
- Single-Level Pass-Through Terminal Blocks: These are used for straightforward wire-to-wire connections, often referred to as single-feed terminal blocks. They are the simplest type, featuring one input contact and one output contact.
- Dual-Level Terminal Blocks: Dual-level terminal blocks have an additional level of connection terminals stacked above the first one. This arrangement is commonly employed to save space while maintaining functionality.
- Three-Level Terminal Blocks: Similar to dual-level blocks, three-level terminal blocks have an extra level at the top. One of the advantages of using multi-level blocks is the ability to make multiple connections within the same block, offering increased versatility and compactness.
WIRE-SECURING METHOD
- Screw clamps: Screw clamps are the industry standard for termination methods. They use screws to tighten the wires and accommodate a variety of wire sizes. They are commonly used in home and commercial wiring for moderate voltage and current needs. Care must be taken not to overtighten as this may damage the cable and cause an unreliable connection.
- Spring Clips: Spring clips use spring force to secure wires. They are a newer alternative to screw clamps and are particularly suitable for applications with limited workspace and smaller wire diameters.
- Blade connections (blade or spade terminals): Blade connections are designed for quick insertion and removal without soldering. They offer ease of use and flexibility.
- Fence terminals: Similar to screw terminals, fence terminals use screws to secure the cable. They usually have multiple terminal points and small obstacles between the various terminals. Barrier terminals are suitable for high-voltage scenarios where arcing or short circuits need to be prevented.
- Push-In Terminals: Push-in terminal blocks use spring-loaded levers that allow cable entry in one direction and prevent disassembly, with the added benefit of preventing over-tightening. However, some may not be reusable and lack disassembly mechanisms, which may pose a challenge for repair efforts.
- Pluggable Terminal Blocks: Pluggable terminal blocks feature cable entries and plug outputs for easy connection to an outlet. They are useful for hot-swappable or removable connections during repair or inspection. Screw contacts with metal plates for holding cables of various sizes are common in pluggable terminals.
TYPES OF TERMINAL BLOCKS AVAILABLE FROM SHINING
High Temperature Ceramic Terminal Blocks (Porcelain Connectors)
Euro Type Feed Through Terminal Blocks
HOW TO DECIDE ON THE TERMINAL BLOCK?
Choosing the right terminal block requires considering these factors and selecting based on the application.
Current requirements:Determine the required current rating and choose a terminal block that can handle the expected current demand, while also considering the need for a safety buffer. Generally, it is recommended to choose a terminal block with a current rating higher than the actual current requirement to prevent overheating and damage to the terminal block.
Voltage requirements:Determine the required voltage rating and choose a terminal block that can handle the expected voltage demand. Additionally, pay attention to the insulation performance of the terminal block to ensure effective isolation between different circuits.
Wire type: Different types of wires have their own advantages and disadvantages, so it is necessary to choose the appropriate wire type based on the application.
Installation method:Different terminal blocks have different installation methods, includingPCB mount,barrier strips, andfeed-through.
Terminal block size:Determine the required terminal block size to ensure that it can accommodate the wires being used and the appropriate terminal blocks.


